So in this Chapter, we will discuss the topics related to AWS ***
Traditional IT Overview
Problems with traditional IT approach:
- Pay for the rent for the data center
- Pay for power supply, cooling, maintenance
- Adding and replacing hardware takes time
- Scaling is limited
- Hire 24/7 team to monitor the infrastructure
- How to deal with disasters? (earthquake, power shutdown, fire…)
Hence, here comes the question: Can we externalize all this?
And the answer is yes. And tha will be the CLOUD.
What is cloud computing
So now let’s talk about cloud computing. So what is cloud computing?
The definition is as such:cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of compute power, database storage, application, and other IT resources.
The very important keyword here is on-demand, you get it when you need it.
And then through a cloud service platform, you’re going to get a pay-as-you-go pricing. That means that you’re only going to pay for what you requested when you requested it and as you’re using it, when you’re done using it, you’re not going to pay anymore.
This is a big shift from traditional IT, right?
Then this is cloud computing. So we can provision exactly the right type and size of computing resources you need.
- Do you need a big server? We have that for you.
- Do you want a small one? We have that too.
- Do you want 10? Yes.
- Do you want two tomorrow? Of course.
The cloud really allows you to adapt to the type and size you need. Then you can access all these resources, not with 24-hour notice, not with two hours notice, but instantly, you don’t need to order things in advance.
When you want a server, and you’ll see this in this course, you’ll have it within seconds.
Then the cloud will also give you a really nice interface so you can easily access your servers, your storage, databases, and a set of application services. Something about the cloud, but in specific AWS, which is Amazon Web Services owns and maintains the network-connected hardware required for these application services while you provision and use what you need via a web application.
So with this interface, we’ll make all these things a reality.
Now, let’s go back to our traditional IT.
So we’re changing. We have our office or our garage, but now instead of building our own data center we’re going to use the cloud, and in the cloud, which is also a data center, is just not our data center, we’re going to have servers one, two, three, as we need and as we go and we’re just going to pay for exactly what we’re using. So you have actually been using the cloud without even knowing it because it is omnipresent, but not necessarily visible.
So if you use a web client such as Gmail, well, for example, it’s an email cloud service and you’re going to pay only for the emails you stored. You’re not provisioning servers when you use Gmail, you just use it. Maybe you’ve stored some data on the cloud, maybe through Dropbox, Google Drive, Google Photos, iCloud, I don’t know.
But with Dropbox, for example, it’s a cloud store service, you’re going to put your files on Dropbox. And originally, fun fact, Dropbox was built on AWS. So we’ve been using a cloud storage service as well without knowing it. And Netflix, it’s huge. It is built entirely on AWS and it provides you a cloud service, which is to get video on-demand. Now, obviously these cloud services are very different from AWS, but we’ll learn what it goes behind these services and how AWS can help you build these kinds of cloud services.
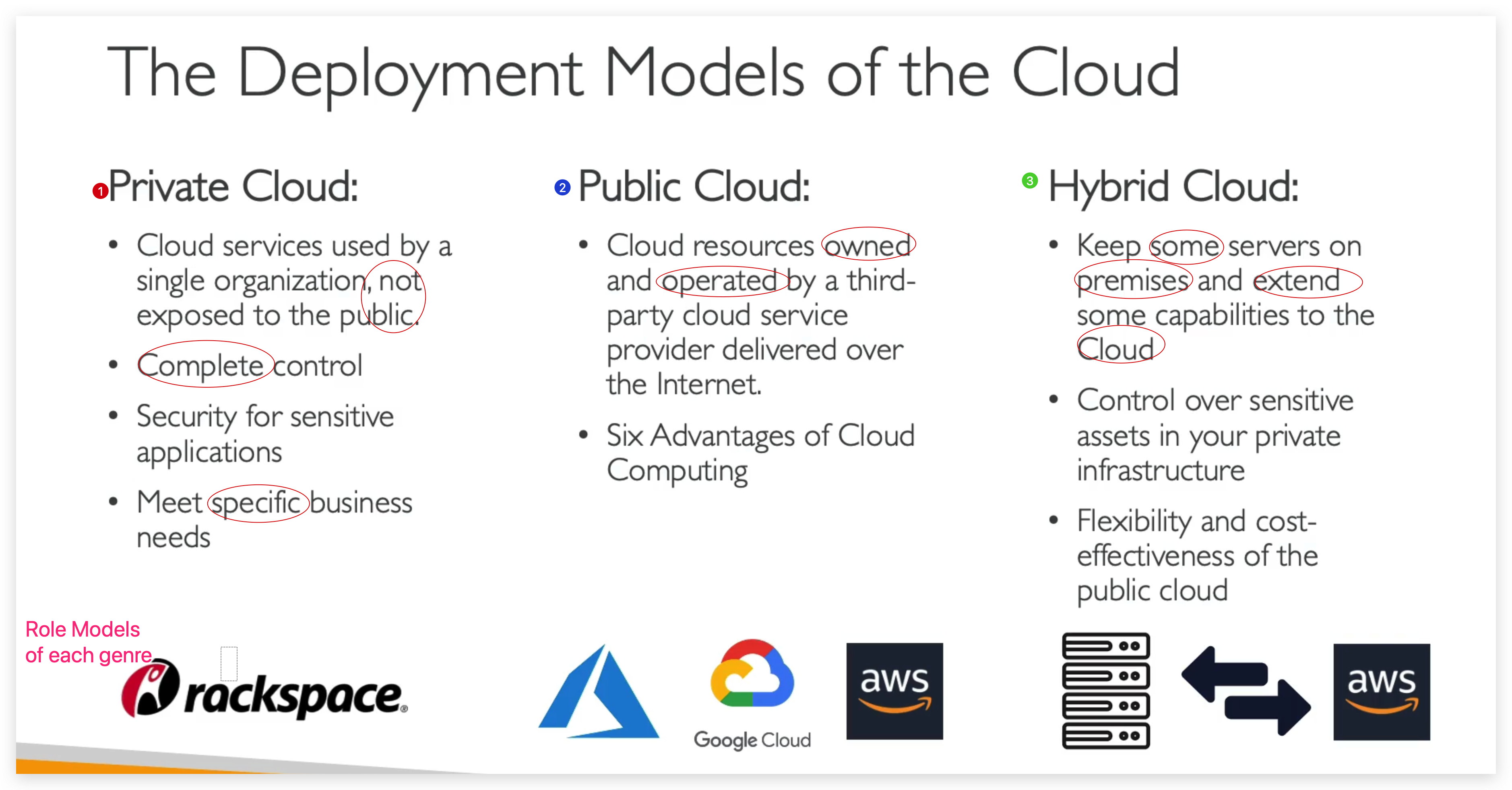
There are different kinds of clouds out there. Clouds can be divided into three categories based on deployment models, namely Private Cloud, Public Cloud and Hybrid Cloud.
private clouds
- used by a single org, not exposed to public
- Complete Control
- Security for sensitive applications
- Meet specific business needs
public clouds
- cloud resources owned and operated by a third party cloud service provider delivered over the internet
- six advantages of Cloud Computing
Hybrid Cloud
- Keep some servers on premises and extend some capabilities to the cloud
- Control over sensitive assets in your private infrastructure
- Flexibility and cost-effectiveness of the public cloud
- Five Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- On-demand self service
- Users can provision resources and use them without human interaction from the service provider.
- Broad network access
- Resources available over the network, and can be accessed by diverse client platforms
- Multi-tenancy and resource pooling
- Multi customers can share the same infrastructure and applications with security and privacy
- Multi customers are serviced from the same physical resources
- Multi customers can share the same infrastructure and applications with security and privacy
- Rapid elasticity and scalability
- Automatically and quickly acquire and dispose resources when we need.
- Quickly and easily scale based on demand.
- Measured service
- Usage is measured, users pay correctly for what they have used.
- On-demand self service
Six Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Trade capital expenses for operational expenses, so CAPEX or OPEX.
- That means that you don’t own hardware, you’re going to pay on-demand and that will reduce your total cost of ownership, your TCO, and your operational expense.
- That means that you don’t buy the hardware in advance, you’re just going to rent it from AWS.
- That means that you don’t own hardware, you’re going to pay on-demand and that will reduce your total cost of ownership, your TCO, and your operational expense.
- Benefit from massive economies of scale.
- Because we are using AWS, not just us, but other customers and so many people are using it, then the prices will be reduced by AWS over time because AWS will be more efficient at running due to its large scale.
- Stop guessing capacity
- Before we had to plan and buy servers in advance and hope that it would meet the capacity, but now we can actually scale automatically based on the actual measured usage for our application.
- Increased speed and agility
- Because everything’s on-demand, We can create, operate and do stuff right away, no blockers for us to be efficient.
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers
- As aforementioned, this will be taken good care of by the AWS.
- Go global in minutes
- This allows a team of say five people to create a global application in minutes, thanks to leveraging the AWS global infrastructure.
Problems Solved by the Cloud
The Different Types of Cloud Computing
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- Provide building blocks for cloud IT
- Provides networking, computers, data storage space
- Highest level of flexibility
- Easy parallel with traditional on-premise IT
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
- Removes the need for your organization to manage the underlying infrastructure
- Focus on the deployment and management of your applications
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- Completed product that is run and managed by the service provider
Based on above explanation, there is a more vivid illustration as below: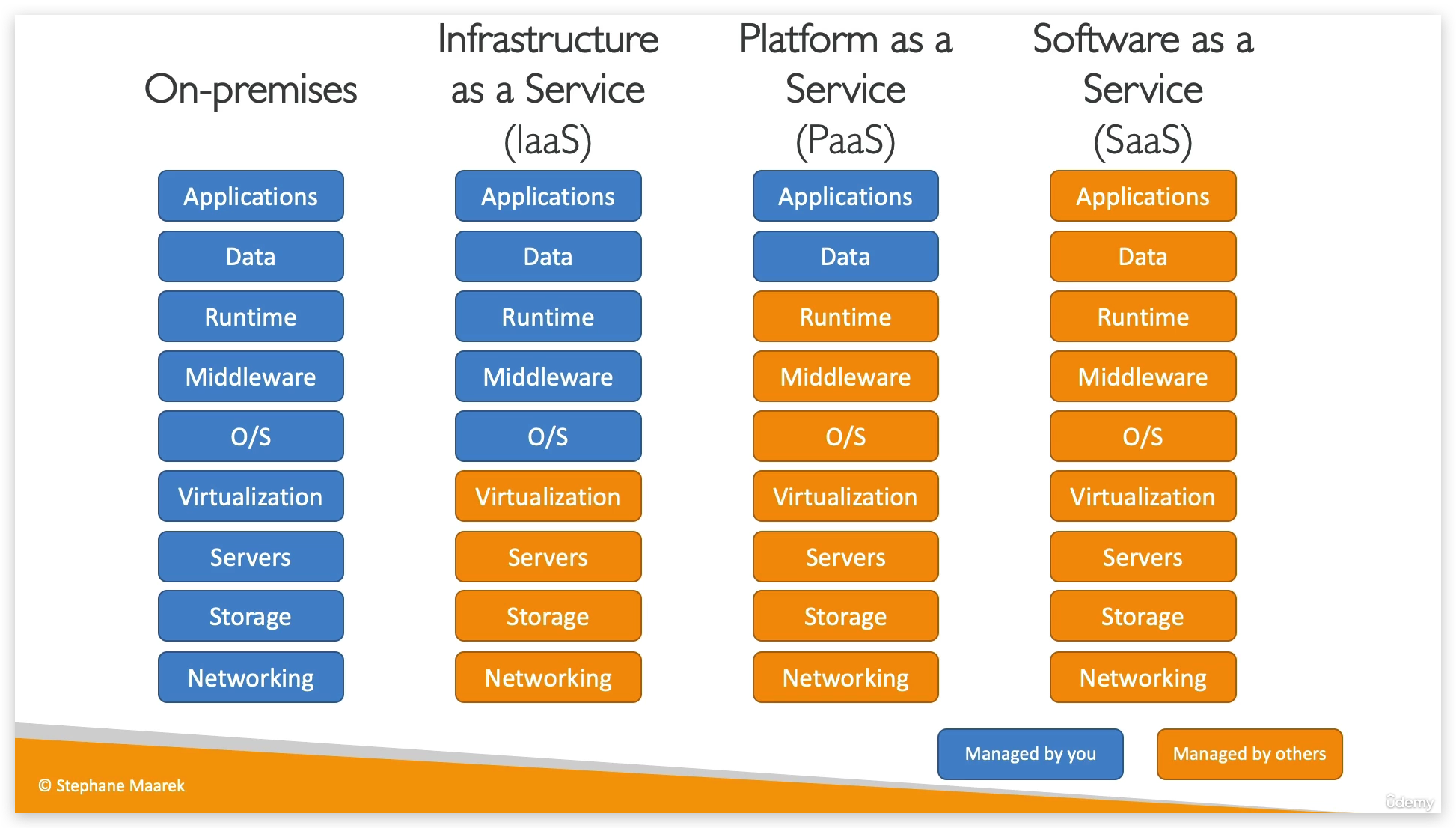
Real world samplers of each cloud type: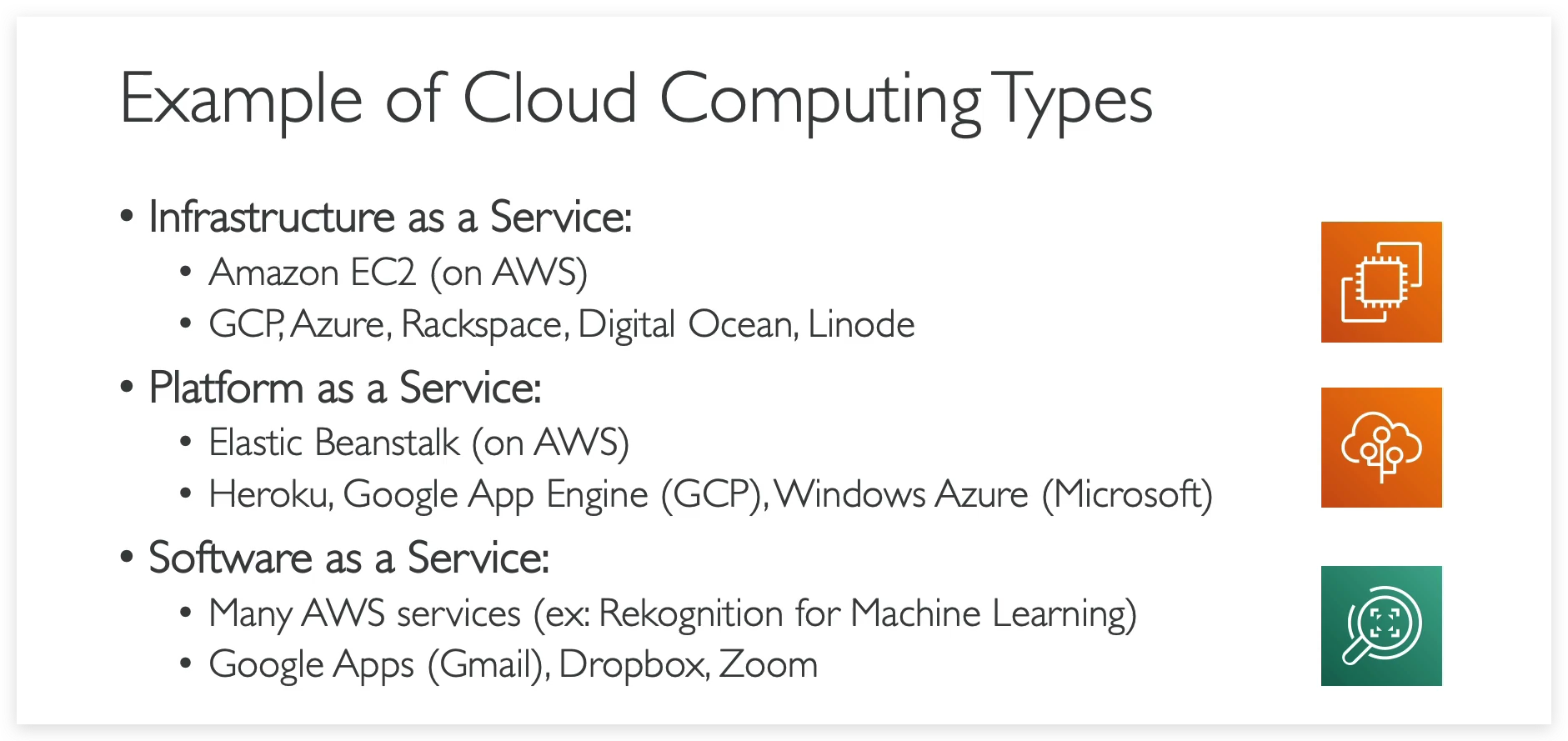
Pricing model of AWS (3 Fundamentals):
AWS-Cloud-Overview
Roadmap of AWS
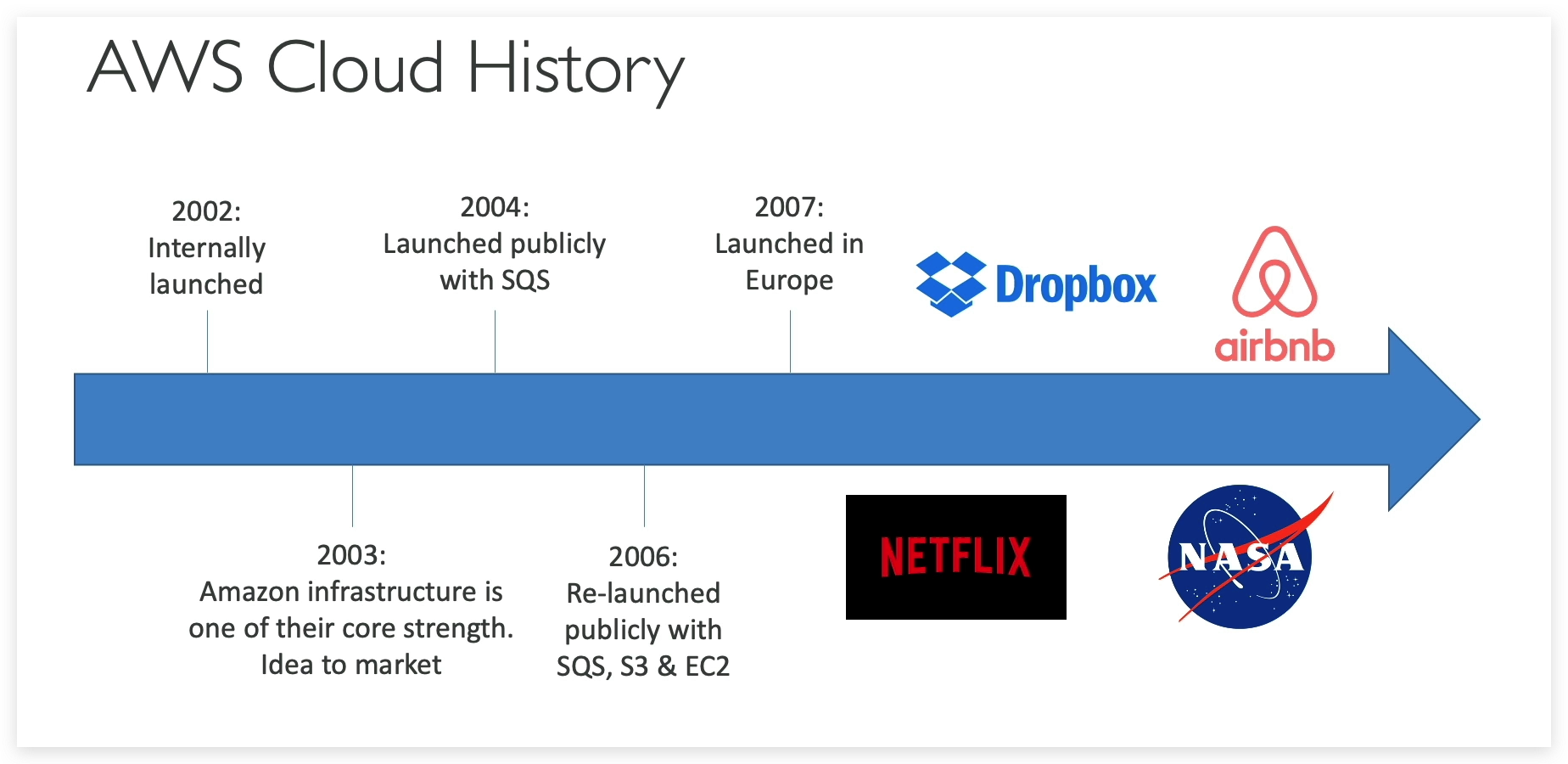
Industry Position
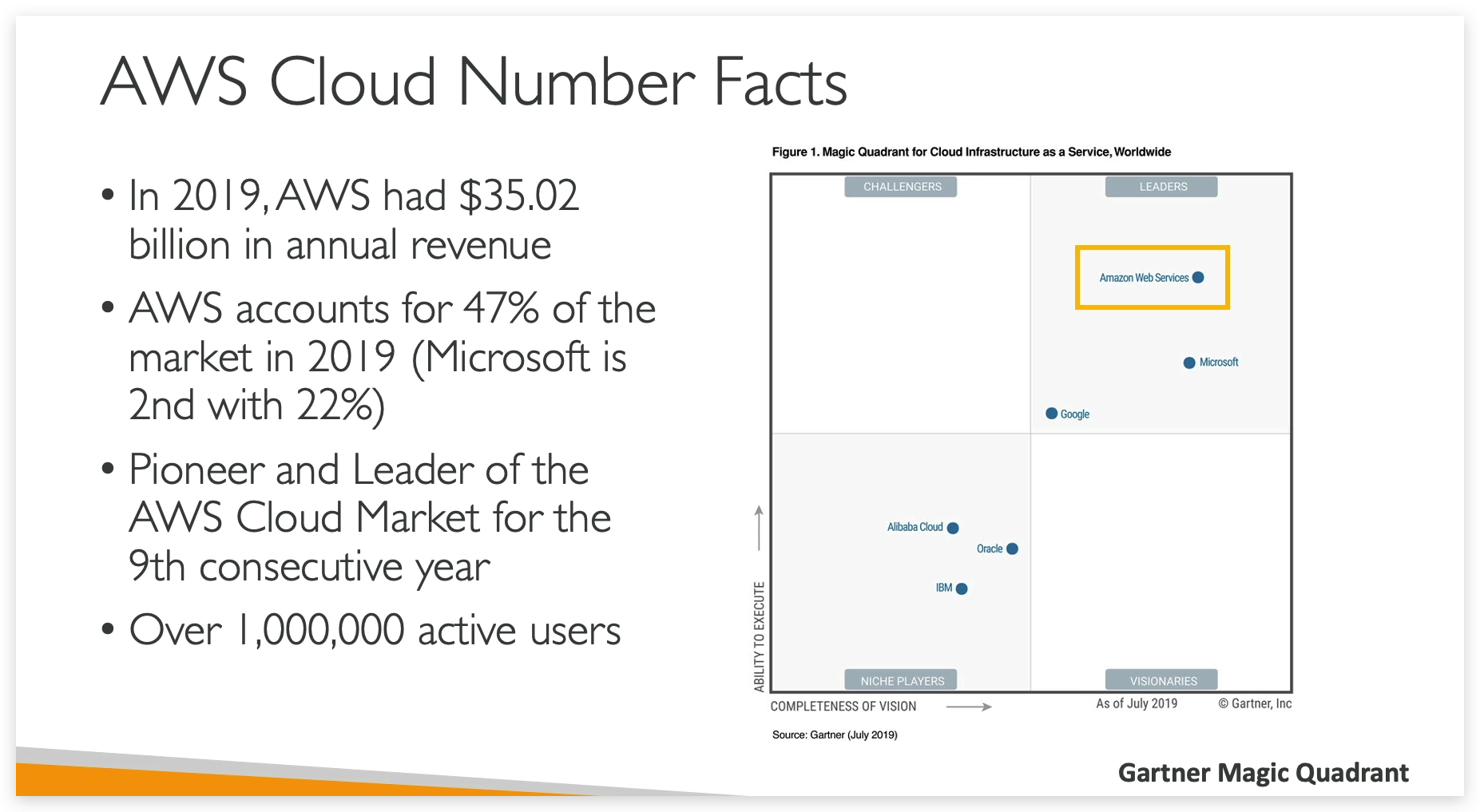
AWS Capability, literally endless

AWS Global Infrastructure
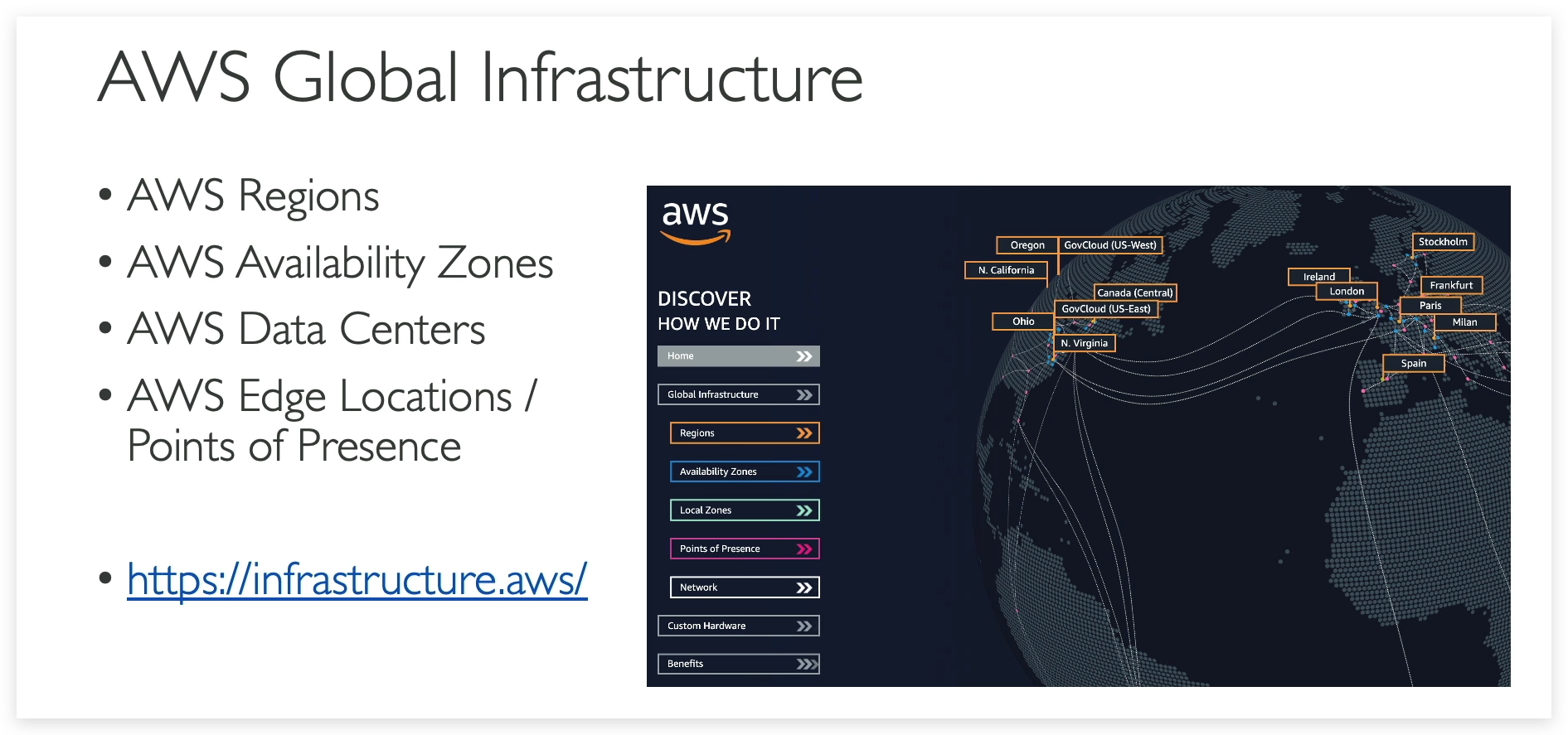
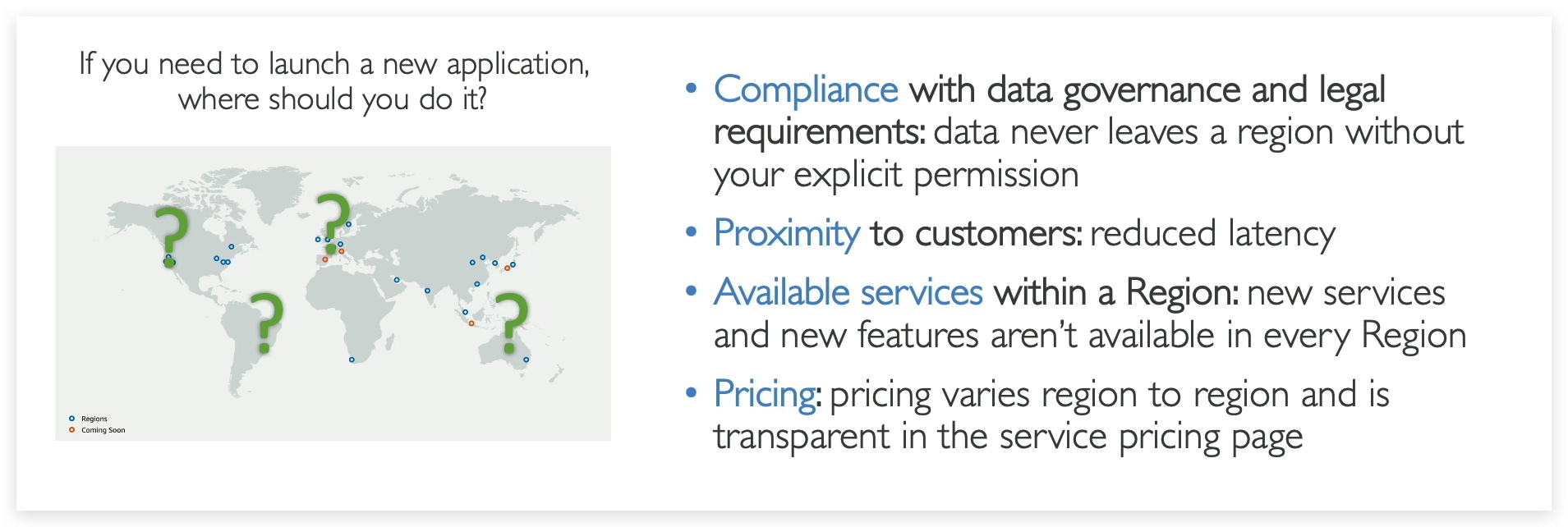
What is a REGION in the context of AWS?
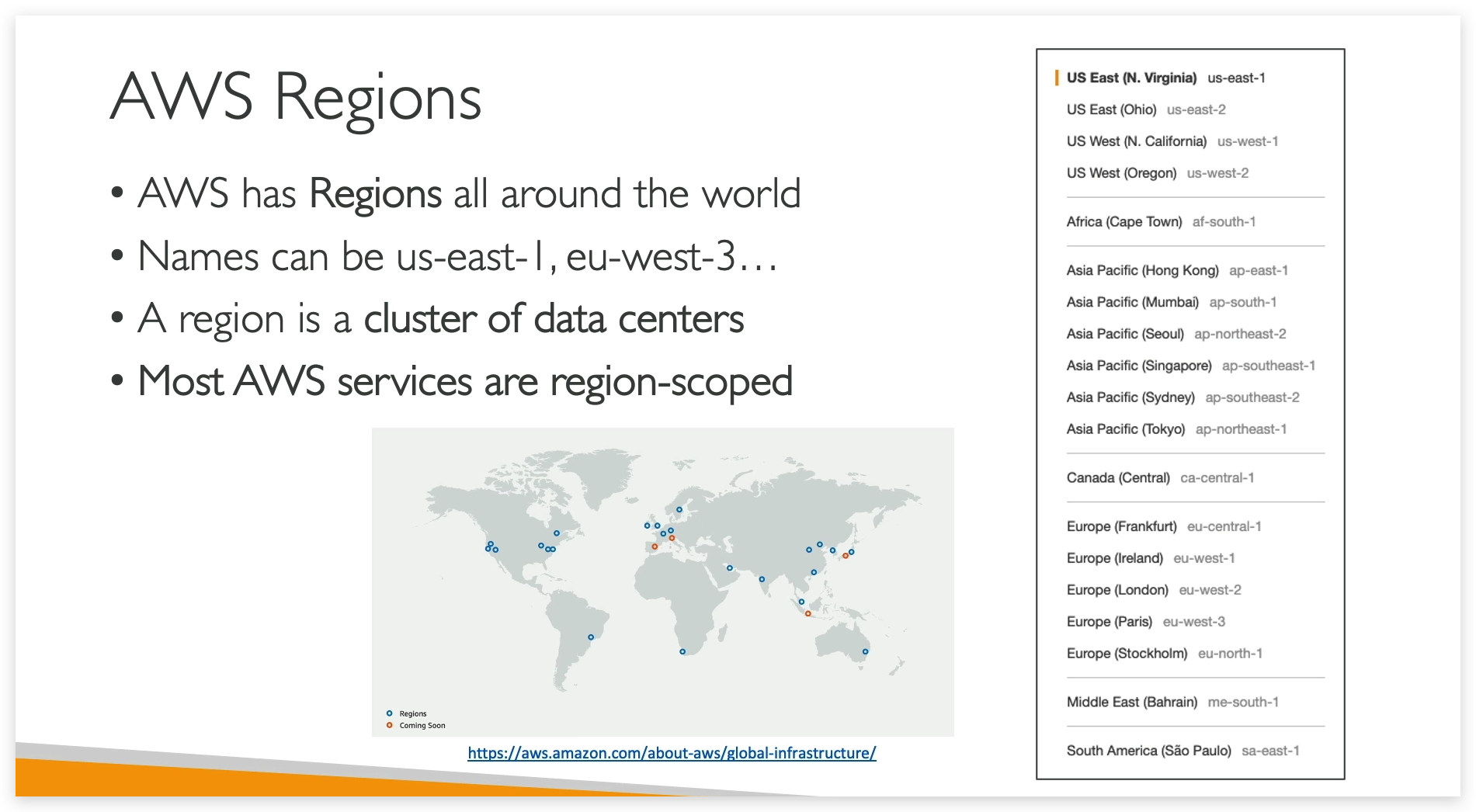
How to choose a Region?
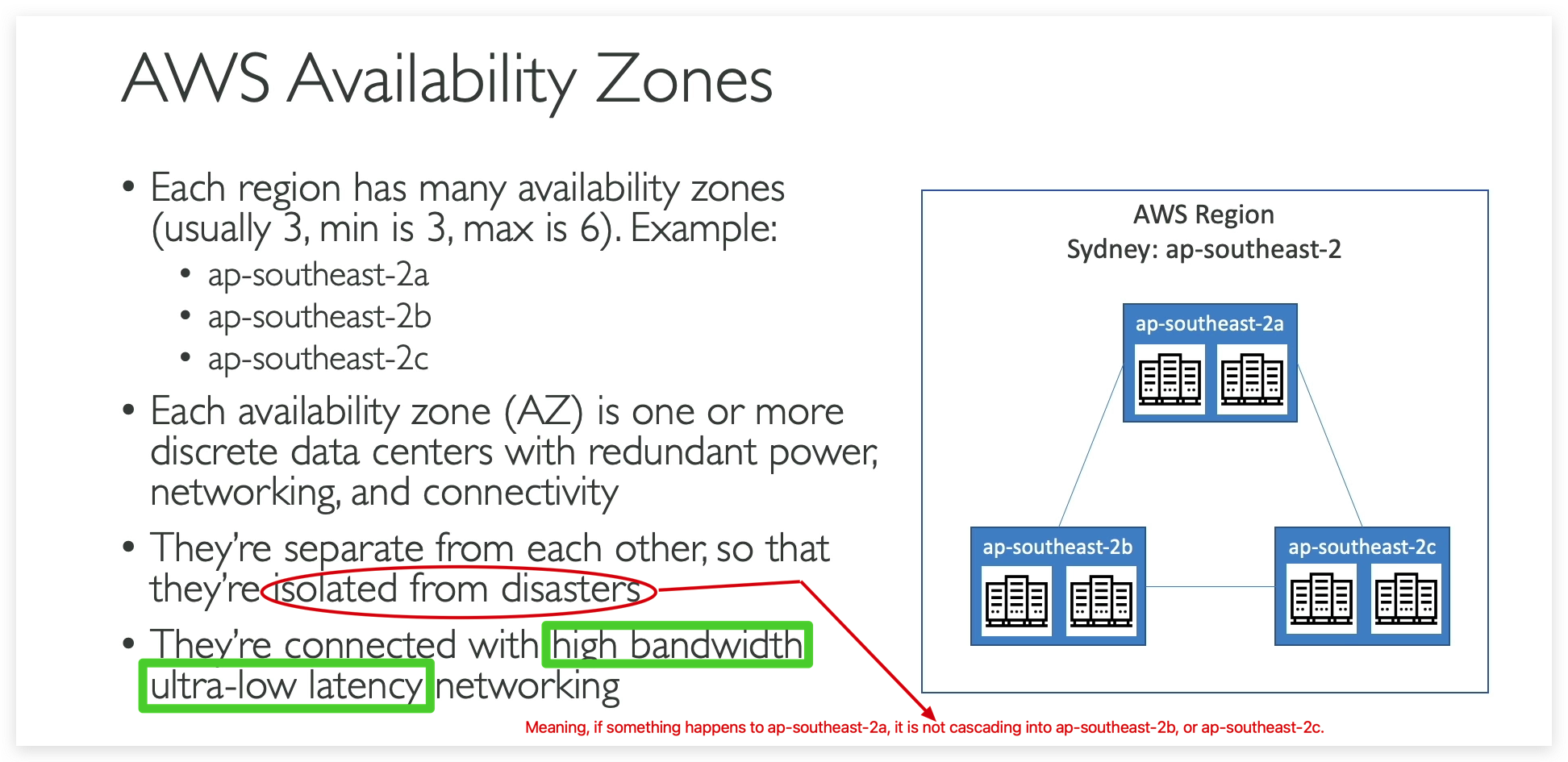
What is AZ (Avalability Zone) and its relationship with Region?
Point of Presence / Edge Locations
Hello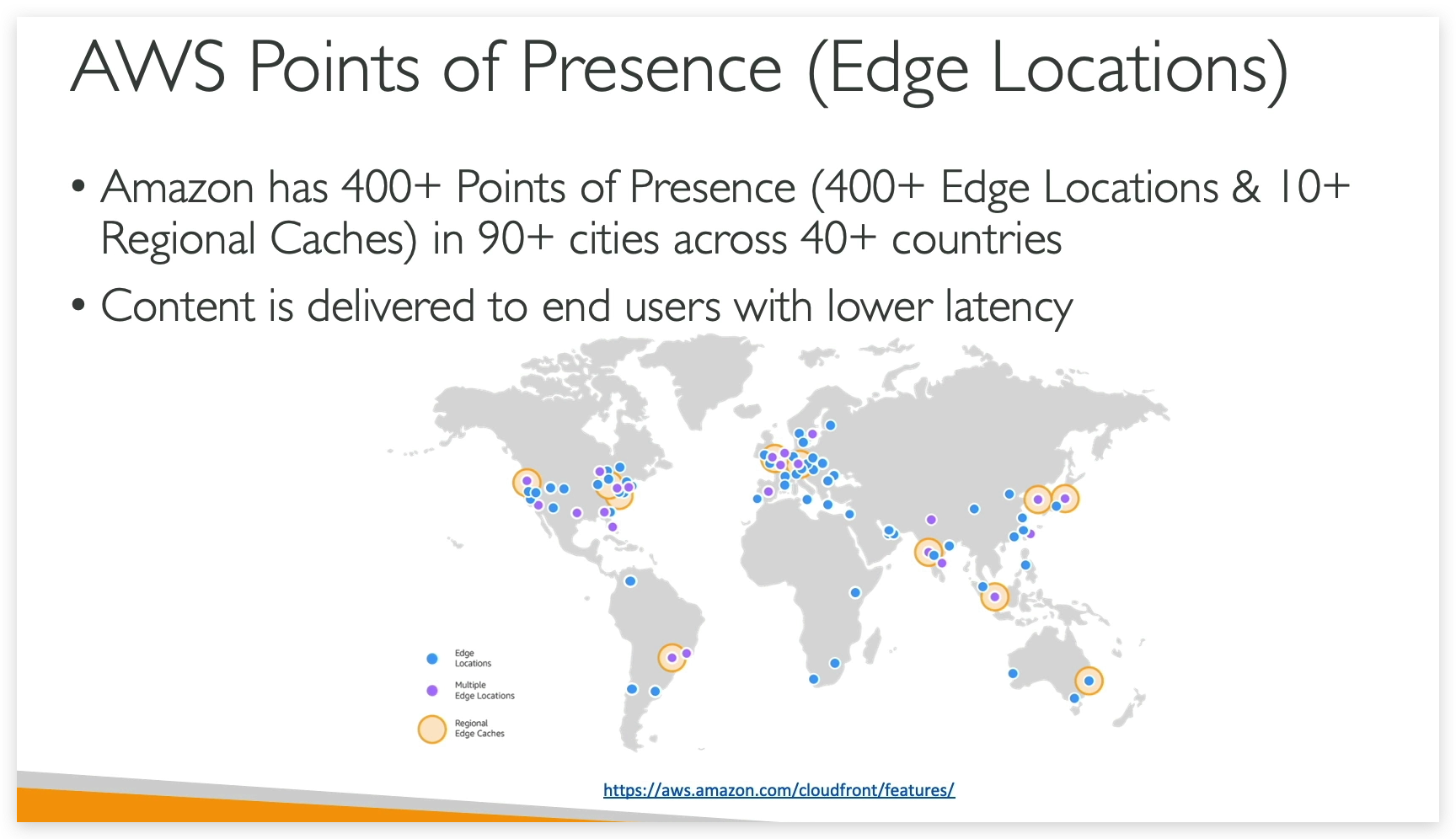
Tour of the AWS Console

Tour of the Console & Services in AWS
Once you logged in,you can switch to a region that are close to you. And you don’t need to be physically in that region to use the services in that region.
In the AWS Console homepage, you’ve got three ways directing to the service page you are intending to.
- Click the “Services” button left to the Top Search bar and then click the “All Services”, then you will see all the services are listed in the right part of the panel in alphabetical order. Till then, you can find the one you need.
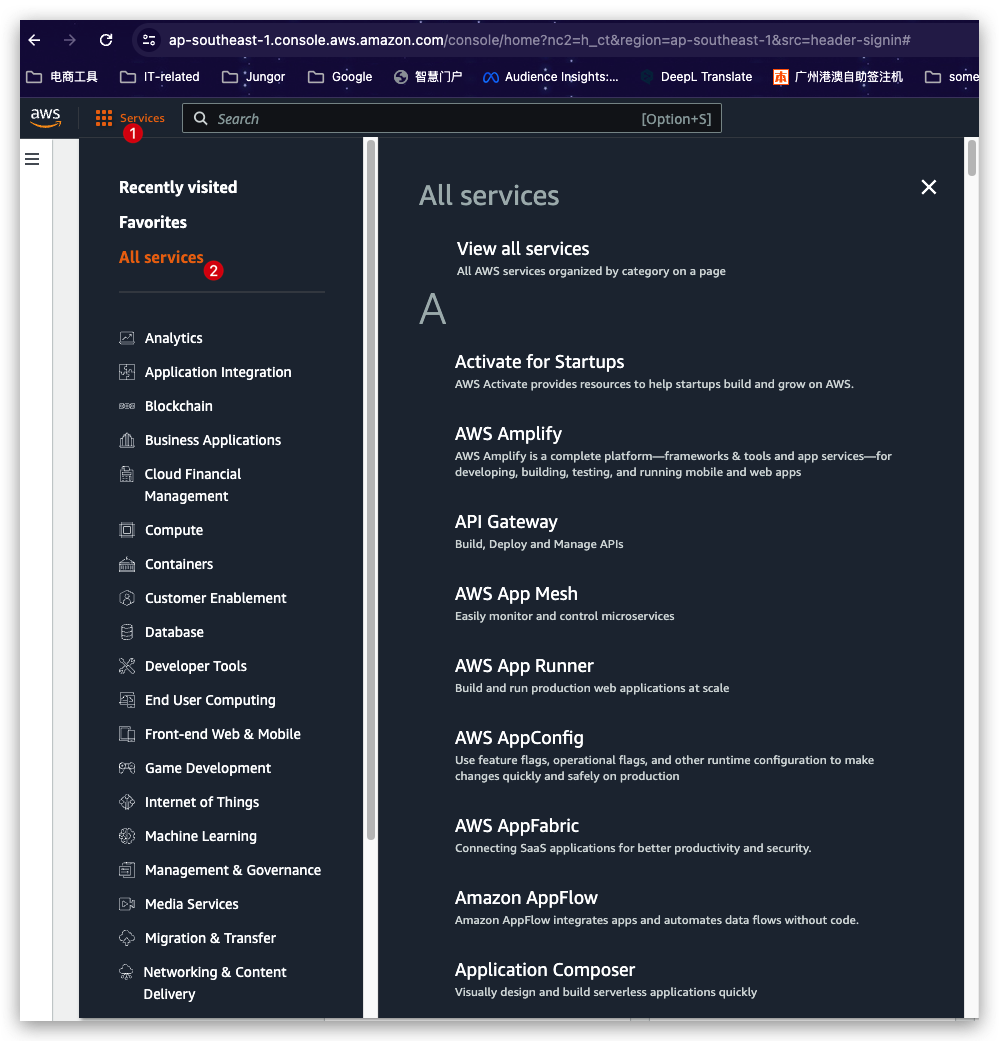
- Click the “Services” button left to the Top Search bar and then click “Compute” to narrow down the genre and finally select the target “EC2”.
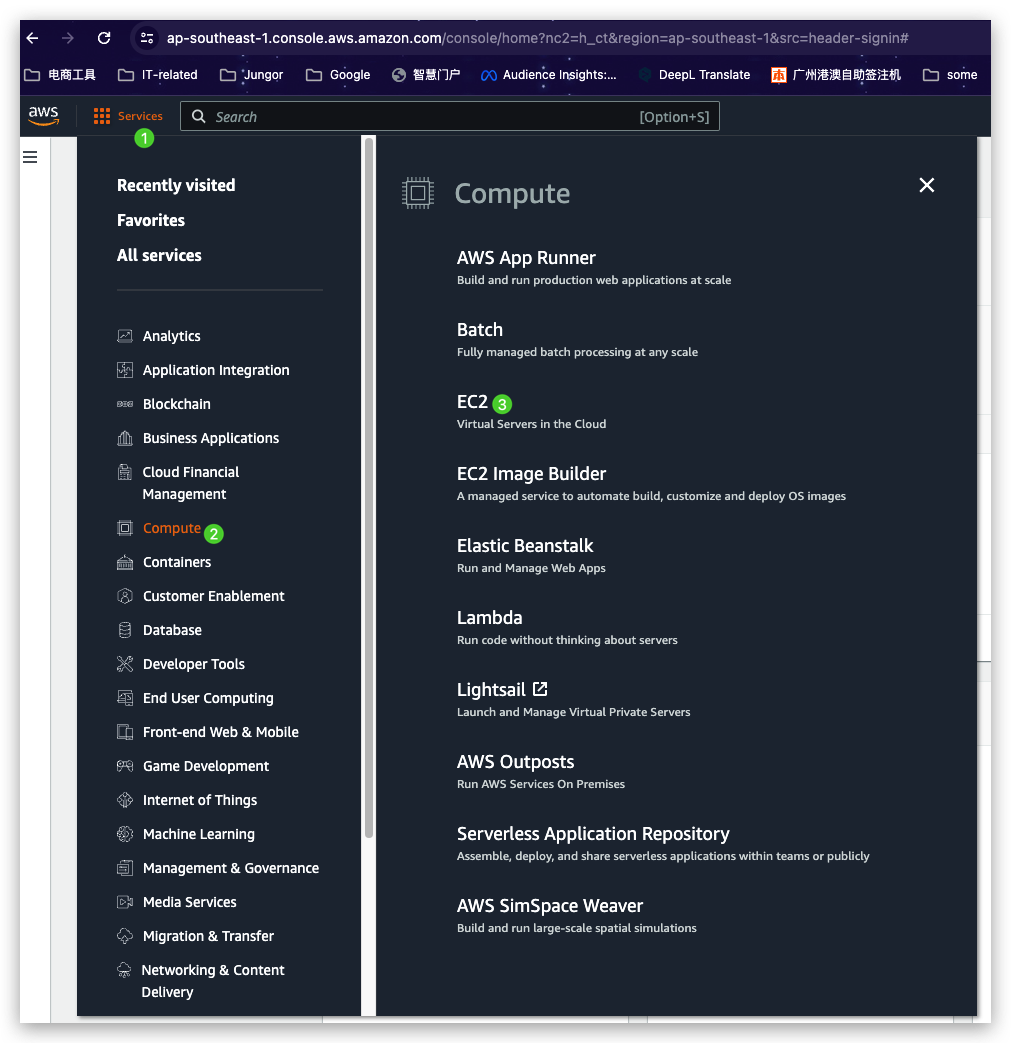
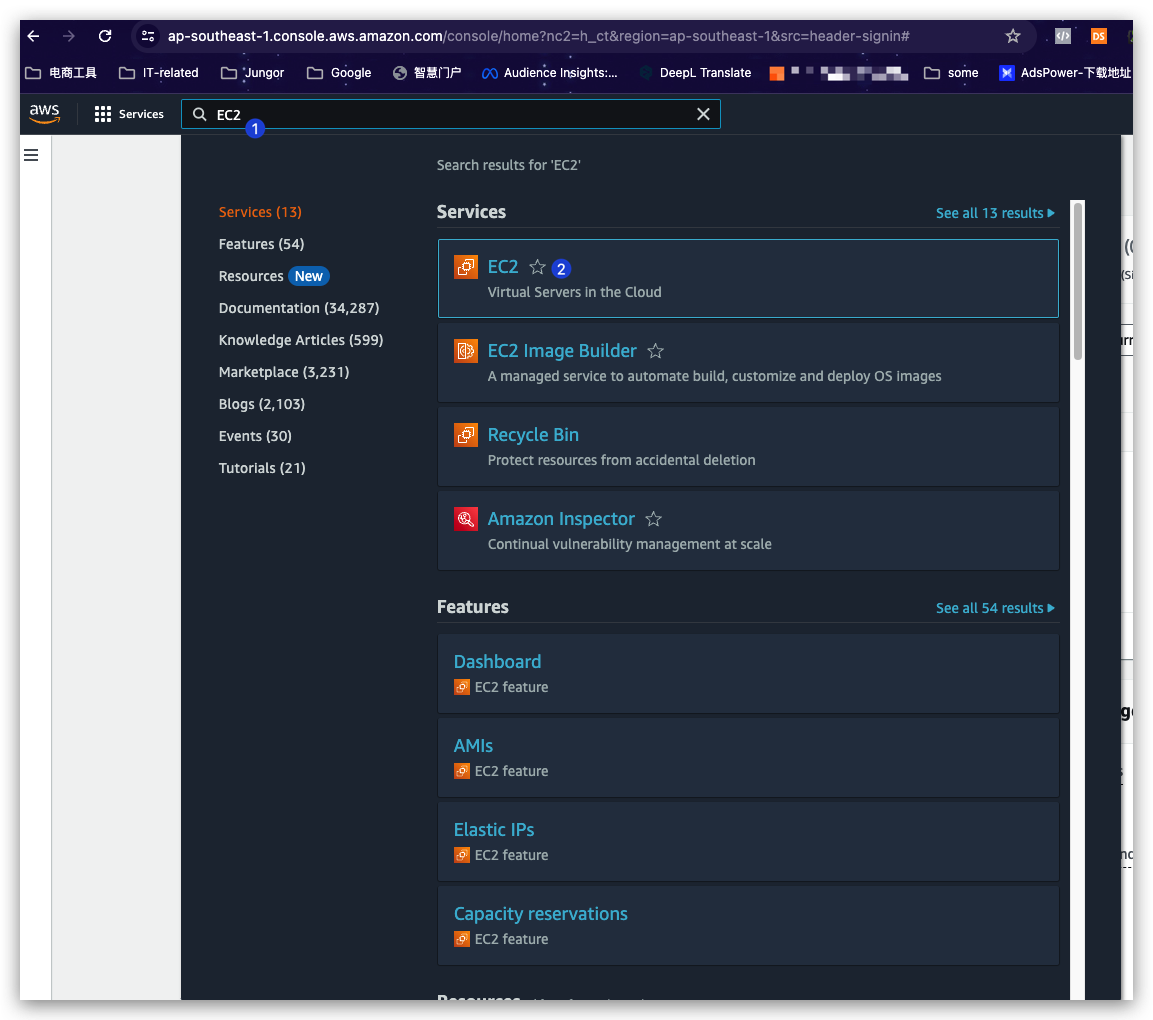
- Directly search the service name in the Top Searching box if you are aware the name.
A service with the region dropdown option shown as “global” by default means this service is a global service that’s accessible to all regions and the layout/view are all the same no matter from which region you visited this service. For example: Route 53. See below.
Similarly, a service with the region dropdown option shown as a certain region name means this service is a regional service that’s ONLY accessible to certain regions and the layout/view might be different if visited from various regions. For example: EC2. See below.
You can check here to see whether a service is available in certain region.
Shared Responsibility Model
Before we move on learning this AWS course, we need to have a look at the Shared Responsibility Model first. This is what define what is your responsibility versus AWS when using the cloud and there is a shared responsibility.
Finally, when you use AWS, you are agreeing to their Acceptable Use Policy, which you can find right here and I think it’s pretty obvious.